Market Overview – Alternative Lending
Alternative Lending (“AL”) generally refers to lending channels, processes, and instruments that have emerged outside of financial services such as regulated banks and capital markets. Alternative lenders are using data science and machine learning to identify quality borrowers that banks haven’t served historically, opening up new revenue streams not captured by traditional Financial Institutions (“FIs”).
Through AL providers, businesses and consumers that normally would not have access to credit with traditional financial institutions can get access to alternative sources of financing. These FinTech lenders leverage high-dimensional alternative data sets and cloud-native, mobile-friendly interfaces to make financing simple, accessible, and instantaneous for consumers and businesses alike.
AL companies are identifying a large portion of the lending market to tap into as 25% of SME owners that apply for loans with traditional banks have their loan applications rejected. Small business owners are taking note of this new lending vehicle with more than 50% aware of financing options beyond traditional banking and 35% of SME loans now coming from AL platforms.
Overall, the FinTech sector has received about $22B in announced PE & VC funding since 2015, and within this sector, companies providing and/or enabling lending services attracted 36% of financing. In this blog we break down the AL market structure, describe dynamics driving growth in the AL ecosystem, and talk about venture funding trends in this space.
Alternative Lending History
In the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, when the convergence of low interest rates and heightened regulation made banks’ lending much more constrained and substantially less profitable, a new wave of technology-based FinTech lenders began to emerge. Through the decade following the crisis, numerous AL companies were formed and successfully grew to become substantial market players.
Alternative Lending Categorization
We identified three major categories in the Alternative Lending market space: (1) Alternative lenders – companies that allow borrowers to obtain credit directly through their offerings – effectively competing with banks; (2) Alternative-lending solutions for FIs – companies offering solutions that enable traditional FIs with AL-capabilities, and (3) Embedded lenders – players that allow non-FI organizations (typically retailers) to offer loans to their own clients.
Alternative lenders
Balance-sheet lenders like Kabbage, OnDeck, and FundThrough offer direct financing agreements, where the lender assumes all risk for the transaction. These players make money through the spread between the capital they borrow and the capital they lend out.
Marketplace lenders like Lending Club and Funding Circle are peer-to-peer (“P2P”) platforms that connect borrowers and lenders. These P2P lenders pool capital from a diverse spectrum of institutional investors to make unsecured loans to consumers and businesses. In these transactions, the lending platform assumes no credit-default risk and passes all of it on to their investors.
Alternative data inputs analyzed by the above AL platforms surpass basic Know Your Customer (KYC) information, credit scores, and other traditional financial inputs. On the consumer side, providers like Plaid and Yodlee look at bank data. Other vendors evaluate income data, utility payment data, and digital fingerprints mined from online activity. On the business-lending side, AL platforms consider non-traditional metrics like monthly sales data, payroll data, and other accounting inputs.
Alternative-lending solutions for FIs
Lending platforms like Ncino, Finastara, and LendingFront provide comprehensive functionalities which enable incumbents to integrate modern FinTech-like lending software into their existing platforms. These solutions help legacy FIs save big on costly and time-intensive digital transformation initiatives. The typical business model of these platforms is Software-as-a-Service (“SaaS”) as it allows for a more seamless integration.
Enabling technologies like Forward.AI, Scienaptic, Conductiv, and FactorTrust offer software tools that allow financial institutions to enhance specific steps in their lending processes: underwriting, credit-risk modeling, predictive analytics, contract lifecycle management, and loan-performance data collection and reporting.
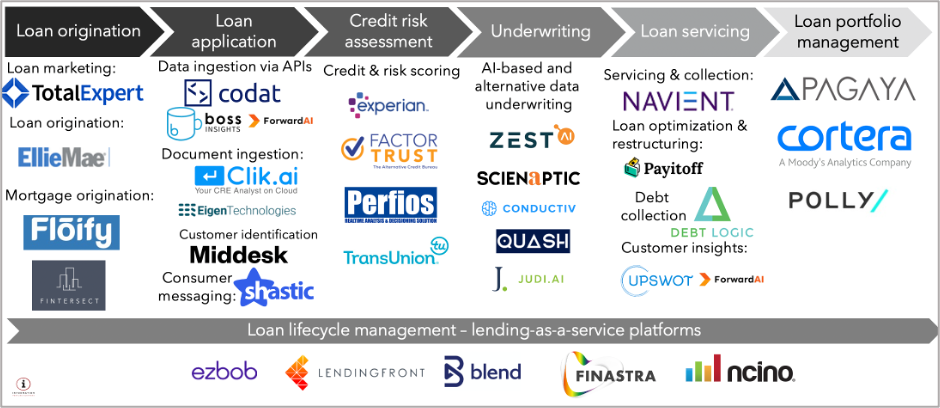
Below we have mapped the high-level ecosystem with example solutions that traditional financial institutions can use to adopt alternative lending tools and approaches, grouped by a lending process step (see pic. 2). Funding of these types of solutions has increased dramatically in the last year, indicating increased investor interest in software solutions that are helping banks compete with AL FinTechs.
Embedded lending
Embedded lending platforms like Lendflow, Klarna, and Afterpay enable retailers to offer credits to their customers. Actual loans are typically provided by partner banks of these FinTechs. Due to the pandemic, this financing model has grown significantly in popularity.
Most AL solutions specialize either on consumer lending or on business loans, with a limited number of players competing in both segments. Alternative lenders and lending solutions also can be categorized by specific types of loans, or on specific types of businesses they lend to (or enable their FI buyers to service better). The market map below shows some examples of companies under this categorization.

Future Outlook
It is interesting to note the differences in performance and valuation multiples of the different types of AL businesses presented above. We found Alternative Lenders to be the most challenging category: multiples are relatively low, and many of these companies struggle with profitability and long-term growth. These kinds of companies take balance sheet risk, require a large volume of capital to grow and must compete with trusted, established brands of traditional financial institutions with diversified revenue streams.
In contrast, companies enabling traditional financial institutions with AL instruments are valued at very healthy multiples aligned with SaaS valuations, averaging at the time of writing at about 20x. Following our investment in LendingFront, a specialist in merchant lending, we continue to be excited about this space as it fits squarely with Information VP’s investment thesis of software for financial institutions.
The most intriguing type is embedded lending. Valuations in this space are very high: one of the leading providers of so called ‘buy now pay later’ (BNPL) solutions, AfterPay, was acquired for a stunning $29 billion by FinTech giant Square. We are watching this space very closely to identify new emerging leaders, although it is yet to be seen if the multiples and valuations will hold at this extreme level.